The Low FODMAP Diet – Your secret weapon!
As a nutrition professional, I am sure you are aware of the low FODMAP diet and FODMAPs, aka fermentable carbohydrates that are found in some foods which are resistant to digestion and instead of being absorbed, they go all the way down your intestine to where your gut bacteria mostly live and can wreak havoc causing a great deal of discomfort for some individuals.
What you may not know is how the Low FODMAP Diet may help those athletes experiencing Exercsie Induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome.
The Low FODMAP Diet & Exercise Induced Gastrointestinal Syndrome
During exercise there is an increased stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system, which reduces gastric emptying and intestinal motility. This can impair the transport of nutrients, which means that if we consume carbohydrate or other nutrients during exercise, the uptake of those nutrients into the body and into circulation may be impaired, which leads to malabsorption.
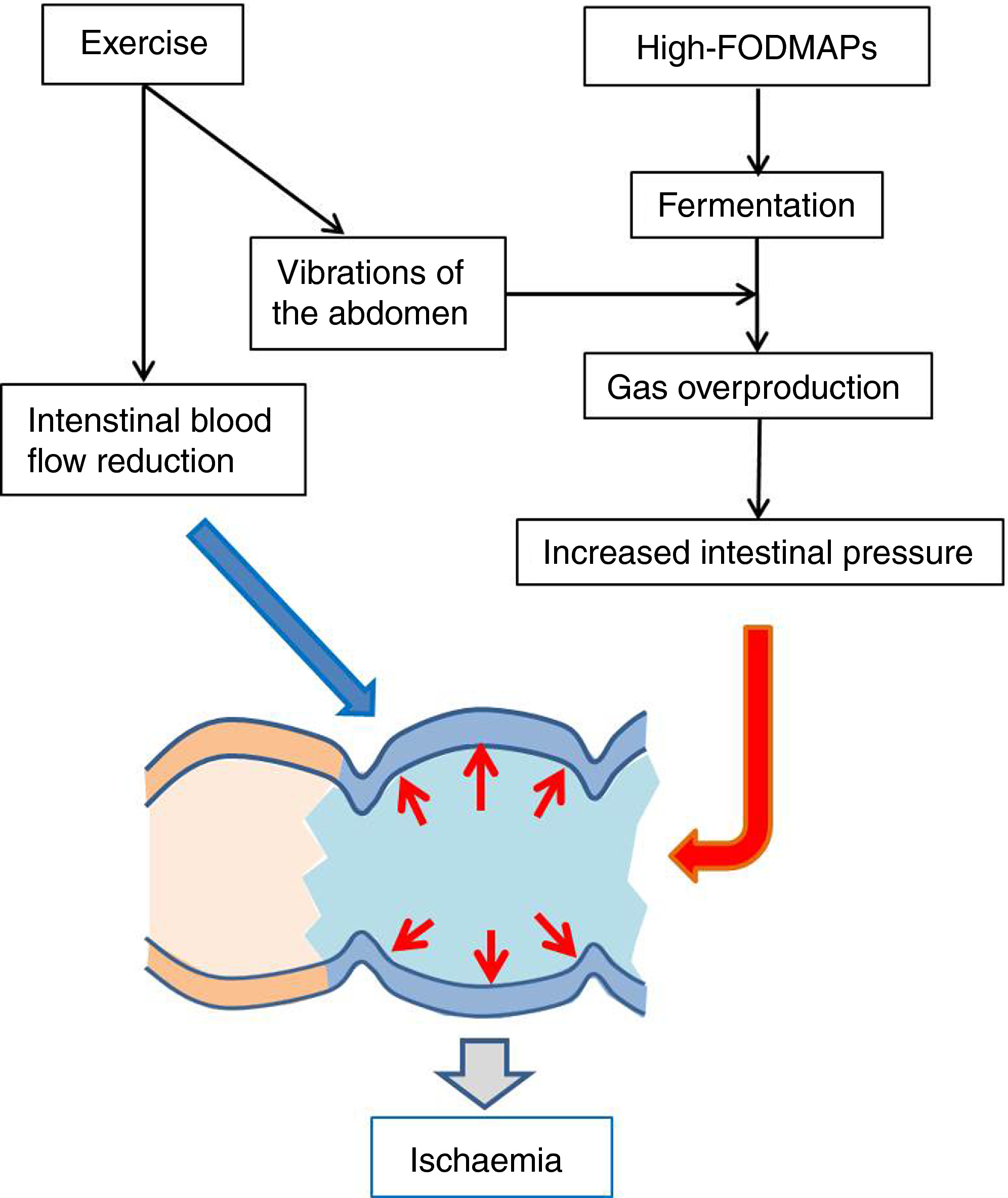
Simultaneously, when we start exercising, blood flow gets prioritised to the muscles to provide them with oxygen and nutrients; alongside blood flow also heading toward the skin surface for cooling. Therefore, there is less oxygen available along the gastrointestinal tract, which creates damage and inflammation to the gut. Those perturbations to the gut are called the exercise-induced gastrointestinal syndrome.
Using a low FODMAP diet 3 days prior to long training sessions, key training sessions & events can reduce the occurrence of exercise induced gastrointestinal syndrome.
During exercise, a reduction in intestinal blood flow occurs in both the small intestine & the colon.
We know consumption of high FODMAP foods causes fermentation and can lead to overproduction of gas. The movement of exercise also increases fermentation reaction rates and generates more gas at a faster speed. (1)
This is why a low FODMAP diet in the lead up to key sessions and events can prevent symptoms as there is a decrease in fermentation, gas production and therefore a decrease in intestinal pressure.
In fact the Low FODMAP diet has shown improved gut symptoms in at least 70% of those who undertake the diet(2). But there is more research needed in this area.
Exercise induced gastrointestinal syndrome is quite complex and simplifying the concepts as well as simply explaining FODMAPs to your clients can be challenging. The good news is that we have two courses dedicated to covering all things FODMAPs and gut issues in athletes.
References